How to Grow Saffron Crocus Corms
Grow Guide #2919
Family: Iridaceae
Binomial name: Crocus sativus
Life Cycle: Perennial
This 'How to Grow' guide details everything a home gardener needs to know to plant, grow and care for Saffron crocus (Crocus sativus).
When to Plant Saffron Crocus Corms
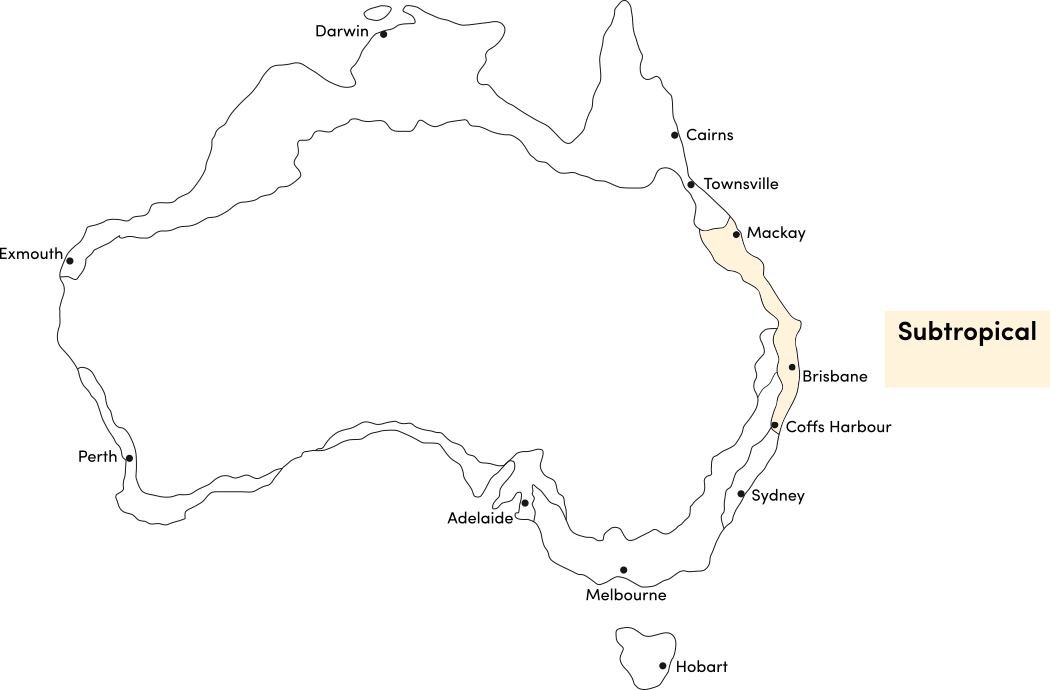
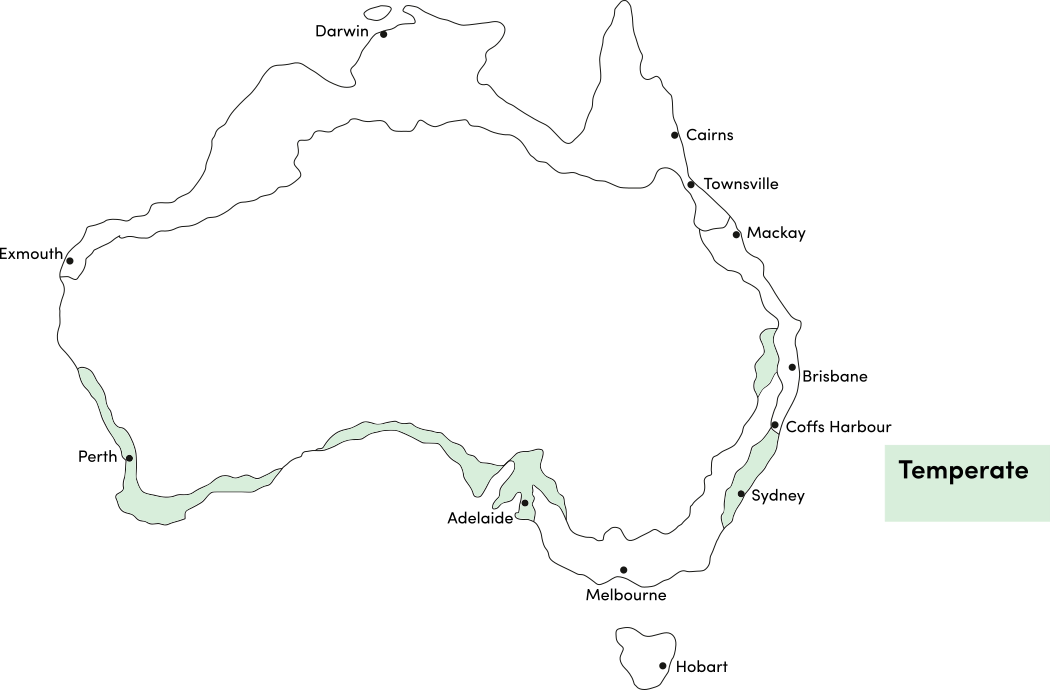
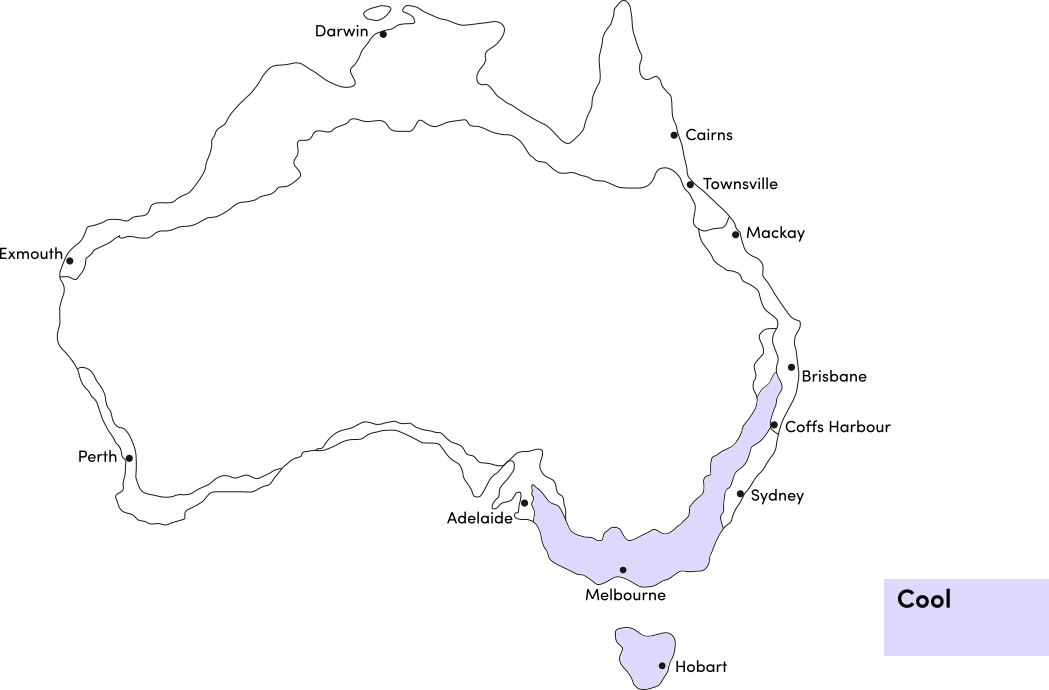
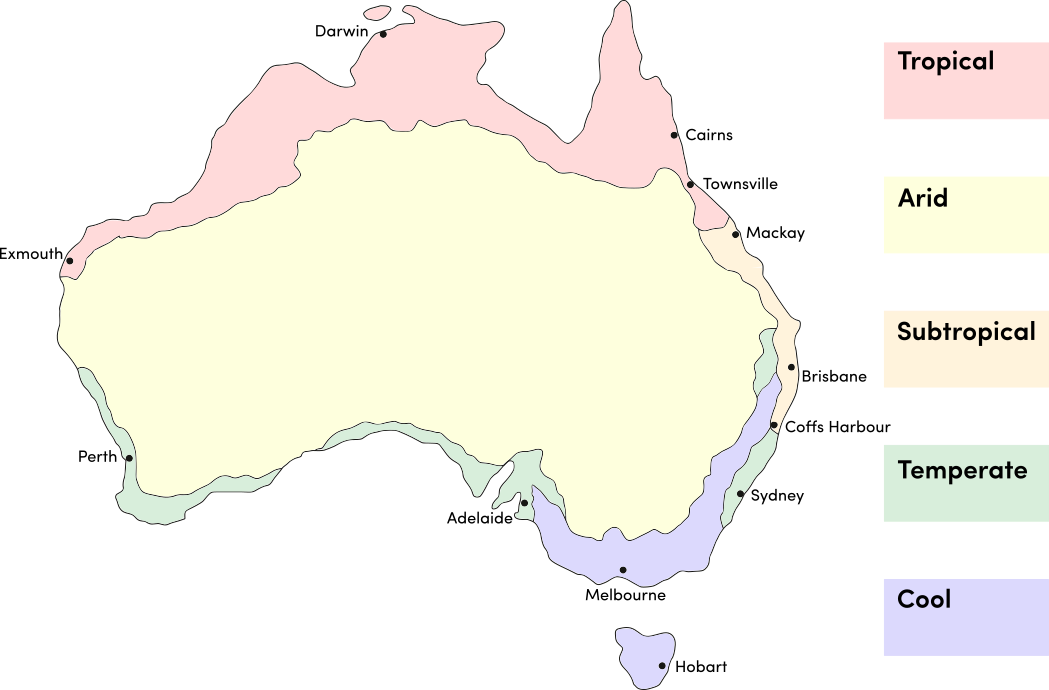
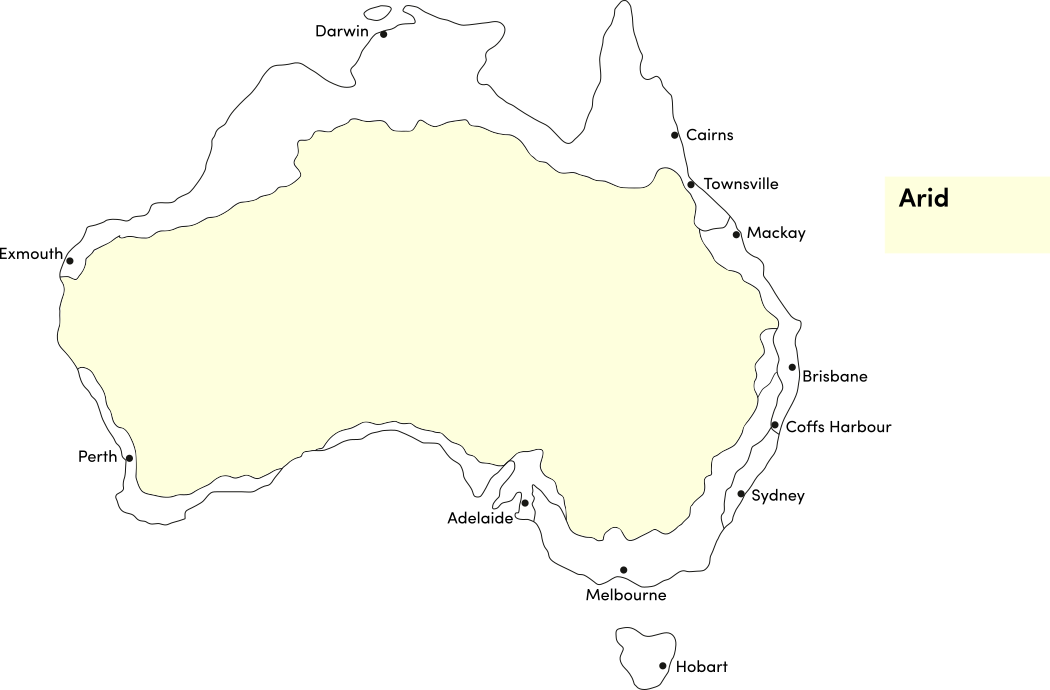
Use the table below to identify the best time of year to plant saffron crocus corms in your climate. Saffron requires a climate with cold winters (with frost) to produce flowers; it is unsuitable for subtropical and tropical climates.
| JAN | FEB | MAR | APR | MAY | JUN | JUL | AUG | SEP | OCT | NOV | DEC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cool | ||||||||||||
| Temperate | ||||||||||||
| Sub-Tropical | ||||||||||||
| Tropical | ||||||||||||
| Arid |
Preparation
Saffron crocus plants are best grown in full sun. Choose a location that will receive at least 6 hours of full sun each day.
Saffron crocus plants need a loose, well drained soil enriched with organic matter. Prepare soil by weeding it thoroughly, digging it over to at least a spade’s depth to loosen the soil, and adding aged animal manure or compost. Organic matter can be dug into heavy soil to lighten it so roots can grow freely. Keep the area free of weeds until planting. Learn more about preparing soil for planting here.
Saffron crocus plants can be grown in containers. If possible choose a variety that’s recommended for container growing. Use a good quality potting mix and make sure your container is large enough for mature plants; a minimum of 20 litres is recommended for saffron crocus. During the growing season, keep in mind that container grown plants may need additional fertiliser to encourage healthy growth.
How to Plant Saffron Crocus Corms
Saffron crocus corms should be planted directly in their final position in the garden or a container.
- Plant individual bulbs 10-15cm apart and 10cm deep with the pointed tip facing upwards.
- Cover with soil and water in well.
- Keep soil moist but not wet until shoots emerge.
How to Grow Saffron crocus
Saffron crocus plants may need watering during the growing season. Water when the soil is dry about 5cm below the surface (test this by scratching away a little soil with your finger). Water deeply in the early morning or late afternoon. Avoid watering the leaves of plants to avoid fungal diseases. Learn more about watering here.
If soil was well prepared no extra fertiliser should be necessary, as bulbs store all the energy needed to bloom from the previous year's growth. In poor soil or to give your plants an extra boost, application of a high-potassium fertiliser or one formulated for flowering plants can be beneficial:
- apply slow release fertiliser at the recommended rate when the first shoots emerge, OR
- apply liquid fertiliser at the recommended rate and frequency when the first shoots emerge.
After flowering, fertilise bulbs with blood and bone or aged or pelletised chicken manure and water in well.
Deadhead or cut saffron crocus flowers regularly during the growing season. Using sharp secateurs or snips, cut flowers for picking with the longest stems possible, or snap off dead flowers. Removing old flowers regularly will direct the plant's energy back into the bulb rather than into the production of seeds.
Leave foliage to die down naturally after flowering; the bulb will absorb the nutrients in the leaves and use them to form the flowers for next season. Once all foliage has died down use sharp secateurs or snips to cut individual leaves at ground level.
Saffron crocus bulbs can remain in the ground for several years without the need to lift and divide them. Mulch heavily to protect bulbs from very hot temperatures over summer. Bulbs can be lifted in areas that experience wet summers, if they become overcrowded or to move them to a different location in the garden.
To lift saffron crocus bulbs, use a garden fork to lift the bulbs from the soil, taking care not to damage them. Prune off any dead leaves still attached to the bulb. Store bulbs in a cool, dry space on a wire rack or in a bag that allows good airflow, such as one made from netting. Temperatures around 20 degrees are ideal for storage; exposure to hot temperatures (over 30 degrees) may affect the viability of the bulbs. Bulbs can be replanted the following season in line with the planting chart above.
How to Harvest Saffron
The flowers will emerge at night and are best harvested in bud stage early the next morning, or when flowers have just opened. Peel back the petals and remove the three red stigmas (also called 'threads'). These are the only part of the flower that is used as a spice or food colouring. Pinch off the stigmas at the base using your fingers or a pair of tweezers.
The saffron threads can be used fresh or dried for longer term storage. To dry the threads, use a dehydrator, heat them gently in the oven at 75°C for a short time, or place them on paper towel and air dry them for 3-5 days. Store dried threads in an air-tight jar or container. Soak dried threads for a few minutes before using them.
Common Problems when Growing Saffron crocus
Like all plants, saffron crocus is susceptible to some pests, diseases and other problems. Below is a list of the most common problems gardeners encounter when growing saffron crocus plants:
 Aphids are small (2-4mm long) sap-sucking insects that congregate on the new shoots or the undersides of leaves. They can cause leaves to wilt or become discoloured, and also excrete honeydew which can attract ants and other insect pests. To manage aphids, remove them by spraying with a garden hose, apply a soap or alcohol spray, or encourage predatory insects to your garden. Read more about aphids here.
Aphids are small (2-4mm long) sap-sucking insects that congregate on the new shoots or the undersides of leaves. They can cause leaves to wilt or become discoloured, and also excrete honeydew which can attract ants and other insect pests. To manage aphids, remove them by spraying with a garden hose, apply a soap or alcohol spray, or encourage predatory insects to your garden. Read more about aphids here..jpg) Rotten bulbs or corms are caused by pathogens entering bulbs or corms after sitting in cold, wet soil, being temporarily waterlogged or being exposed to warm temperatures in winter. They may show obvious signs of rot, have no roots or shoots, or produce stunted yellow leaves but no flowers. Plant bulbs and corms in free-draining soil, raised garden beds or containers; do not water while dormant; and lift and store them if recommended for your climate.
Rotten bulbs or corms are caused by pathogens entering bulbs or corms after sitting in cold, wet soil, being temporarily waterlogged or being exposed to warm temperatures in winter. They may show obvious signs of rot, have no roots or shoots, or produce stunted yellow leaves but no flowers. Plant bulbs and corms in free-draining soil, raised garden beds or containers; do not water while dormant; and lift and store them if recommended for your climate. Slugs and snails are molluscs that feed on tender leaves and shoots, mostly at night, leaving slimy trails behind them. Control them by removing their hiding places, keeping free range poultry, collecting them by torchlight or by placing traps. Read more about slugs and snails here.
Slugs and snails are molluscs that feed on tender leaves and shoots, mostly at night, leaving slimy trails behind them. Control them by removing their hiding places, keeping free range poultry, collecting them by torchlight or by placing traps. Read more about slugs and snails here.
.png)