How to Grow Zucchini Seeds
Grow Guide #2338
Family: Curcurbit
Binomial name: Cucurbita pepo
Life Cycle: Annual
This 'How to Grow' guide details everything a home gardener needs to know to plant, grow and care for Zucchini (Cucurbita pepo).
When to Sow Zucchini Seeds
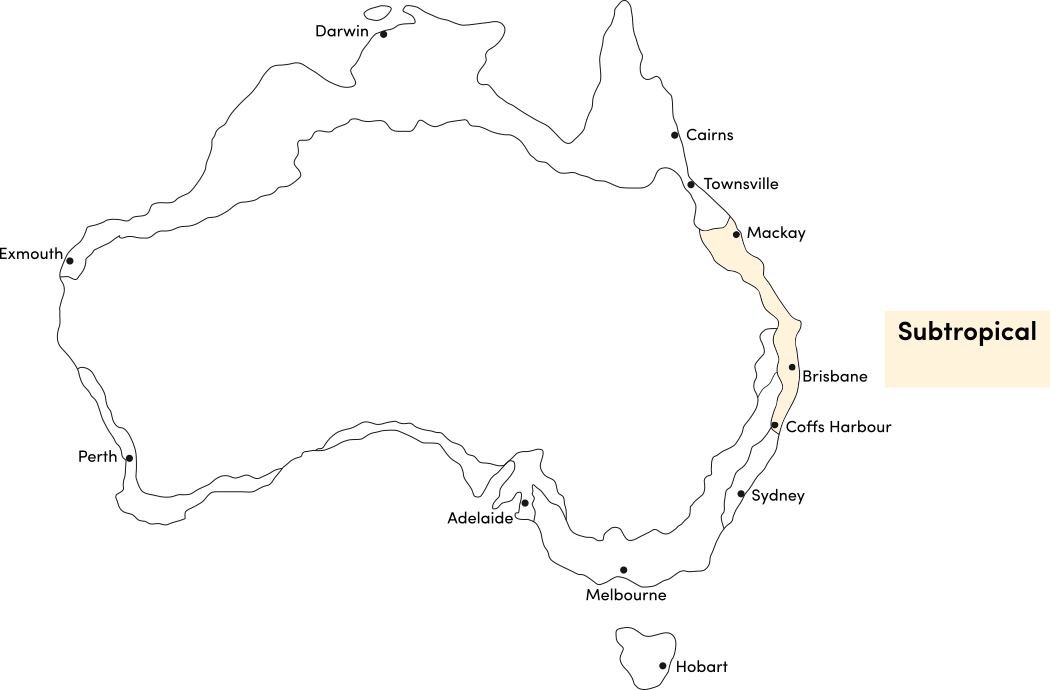
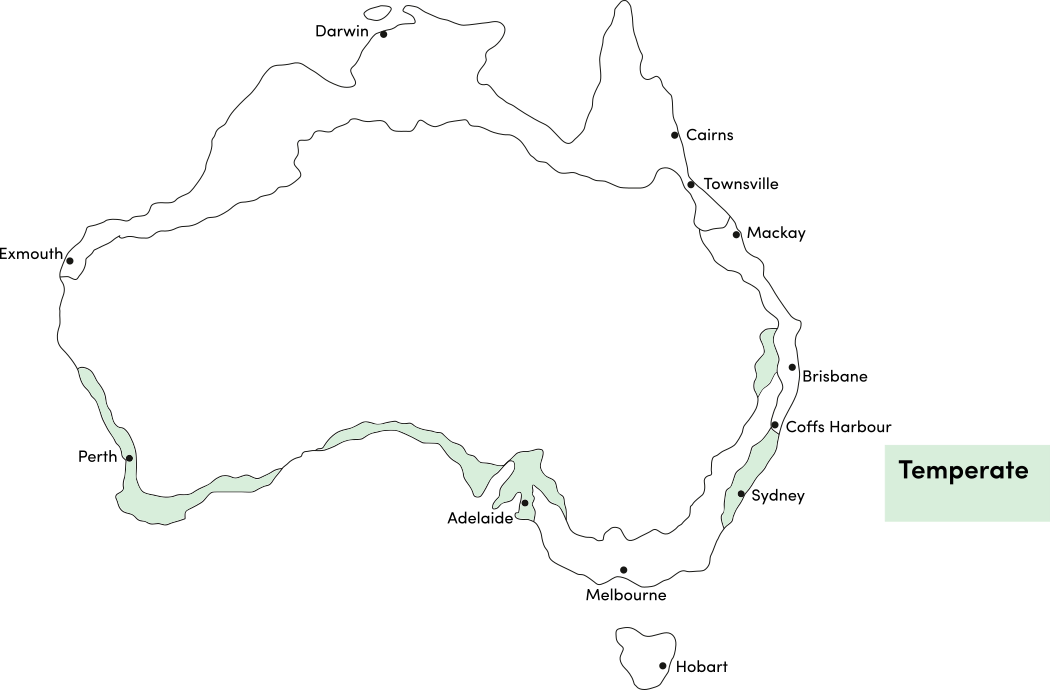
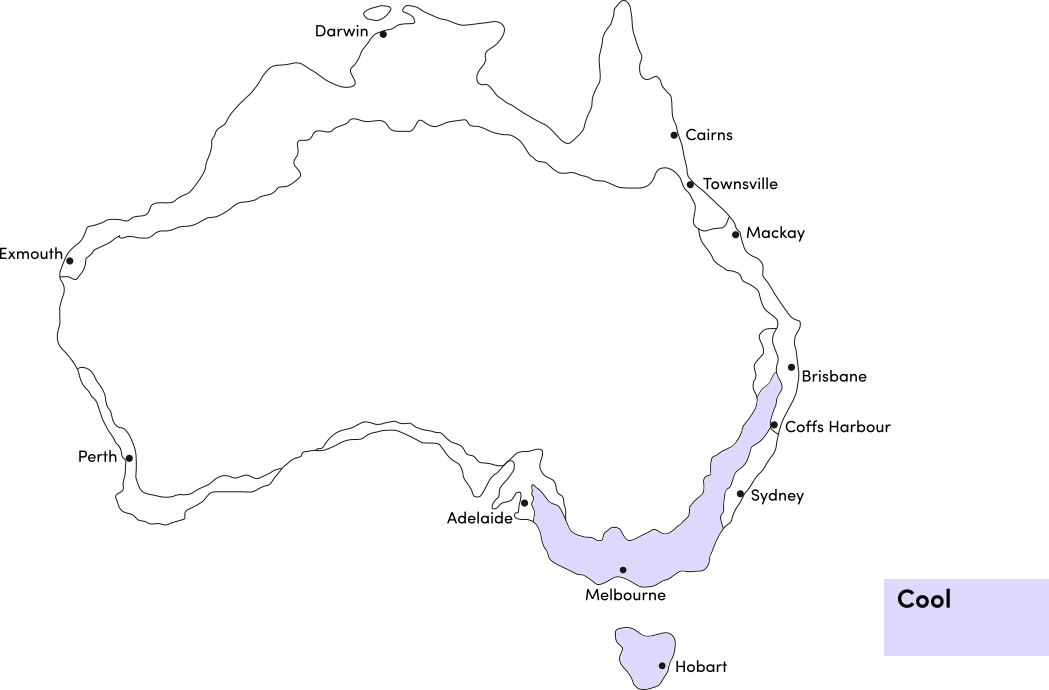
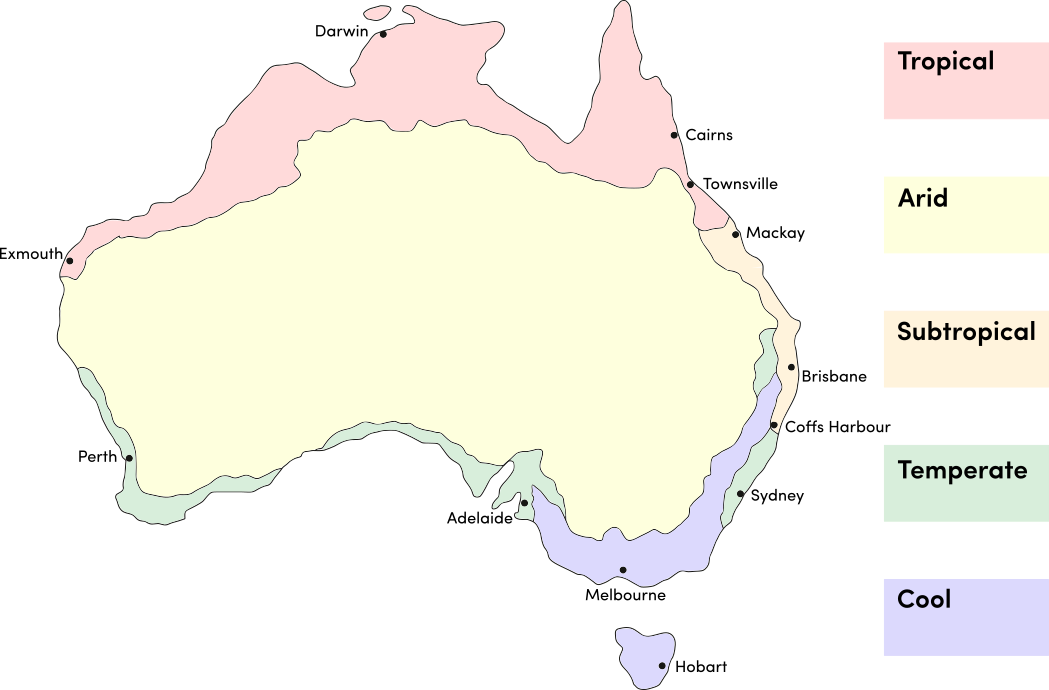
Zucchini is a warm season crop. Use the table below to identify the best time of year to sow zucchini seeds in your climate.
| JAN | FEB | MAR | APR | MAY | JUN | JUL | AUG | SEP | OCT | NOV | DEC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cool | ||||||||||||
| Temperate | ||||||||||||
| Sub-Tropical | ||||||||||||
| Tropical | ||||||||||||
| Arid |
Preparation
Zucchini plants are best grown in full sun. Choose a location that will receive at least 6 hours of full sun each day.
Zucchini plants need a well drained soil enriched with plenty of organic matter. Prepare soil by weeding it thoroughly, digging it over to loosen it and adding aged animal manure or compost. Keep the area free of weeds until planting. Learn more about preparing soil for planting here.
How to Sow Zucchini Seeds
Zucchini seeds do not require any treatment (eg soaking, stratification) before sowing.
Zucchini seeds grow best when they are sown directly into the garden.
- Sow seeds directly in the garden 20mm deep and 50-80cm apart, with rows 80-120cm apart.
- Keep soil moist but never wet or dry.
- Seeds should germinate in around 7-14 days at a soil temperature of 21-35°C.
- Young seedlings will need protection from pests, pets and weather until they are established.
Zucchini is a tender crop that’s sensitive to frost. Do not transplant seedlings or sow seeds outside until all danger of frost has passed.
Optional: In cool climates zucchini seeds can be sown indoors 6 weeks before the last expected frost. Grow them in a warm position with plenty of natural light.
How to Grow Zucchini
Zucchini plants may need watering during the growing season. Water when the soil is dry about 5cm below the surface (test this by scratching away a little soil with your finger). Water deeply in the early morning or late afternoon. Avoid watering the leaves of plants to avoid fungal diseases. Learn more about watering here.
If soil was well prepared no extra fertiliser should be necessary. In poor soil or to give your plants an extra boost, application of a balanced fertiliser or one formulated for fruit and vegetables can be beneficial:
- Apply slow release fertiliser at the recommended rate when transplanting or when seedlings are 5-10cm tall.
- Apply liquid fertiliser at the recommended rate and frequency while plants are fruiting or flowering.
How to Harvest Zucchini
Fruit is ready to harvest when the skin is glossy and the fruit is large enough to eat. Harvest fruit when tender and young as older fruit can become unpalatable. Harvest fruit by cutting it from the vine or bush, leaving a small amount of stem attached. For short term storage, harvested fruit can be kept in the fridge. For long term storage, fruit can be frozen, canned or pickled.
Common Problems when Growing Zucchini
Like all plants, zucchini is susceptible to some pests, diseases and other problems. Below is a list of the most common problems gardeners encounter when growing zucchini plants:
 Blossom end rot is a nutrient deficiency caused by a lack of calcium uptake, often due to inconsistent watering. Fruit will discolour from the bottom end upwards, with the affected area growing darker and harder. Dispose of affected fruit, water regularly and evenly, and correct soil pH and nutrients if required. Read more about blossom end rot here.
Blossom end rot is a nutrient deficiency caused by a lack of calcium uptake, often due to inconsistent watering. Fruit will discolour from the bottom end upwards, with the affected area growing darker and harder. Dispose of affected fruit, water regularly and evenly, and correct soil pH and nutrients if required. Read more about blossom end rot here..jpg) Not setting fruit is a problem caused by lack of pollination. Flowers may fall off the plant or small fruit may form but then shrivel and rot. Wait until the plant is producing both male and female flowers. Use a paintbrush to transfer pollen from the male flowers to the female ones. Learn more about hand pollination here..
Not setting fruit is a problem caused by lack of pollination. Flowers may fall off the plant or small fruit may form but then shrivel and rot. Wait until the plant is producing both male and female flowers. Use a paintbrush to transfer pollen from the male flowers to the female ones. Learn more about hand pollination here.. Possums, birds and other animals can ruin a large percentage of your harvest overnight. Physically exclude pests by using netting or cages, or try spraying plants with a pungent homemade spray made from garlic, fish oil or mustard.
Possums, birds and other animals can ruin a large percentage of your harvest overnight. Physically exclude pests by using netting or cages, or try spraying plants with a pungent homemade spray made from garlic, fish oil or mustard..jpg) Powdery mildew is caused by fungal spores reproducing on the leaves of plants. First showing as white spots on leaves, affected areas can spread quickly to cover the entire leaf surface. While rarely fatal, powdery mildew can reduce yields. Water plants at soil level (not on leaves) to prevent spreading spores, allow good air flow between plants, remove affected leaves and if necessary spray with an appropriate fungicide or homemade spray. Read more here about powdery mildew here.
Powdery mildew is caused by fungal spores reproducing on the leaves of plants. First showing as white spots on leaves, affected areas can spread quickly to cover the entire leaf surface. While rarely fatal, powdery mildew can reduce yields. Water plants at soil level (not on leaves) to prevent spreading spores, allow good air flow between plants, remove affected leaves and if necessary spray with an appropriate fungicide or homemade spray. Read more here about powdery mildew here.
.png)