How to Grow Strawberry Spinach Seeds
Grow Guide #2498
Family: Amaranthaceae
Binomial name: Chenopodium foliosum
Life Cycle: Annual
This 'How to Grow' guide details everything a home gardener needs to know to plant, grow and care for Strawberry spinach (Chenopodium foliosum).
When to Sow Strawberry spinach Seeds
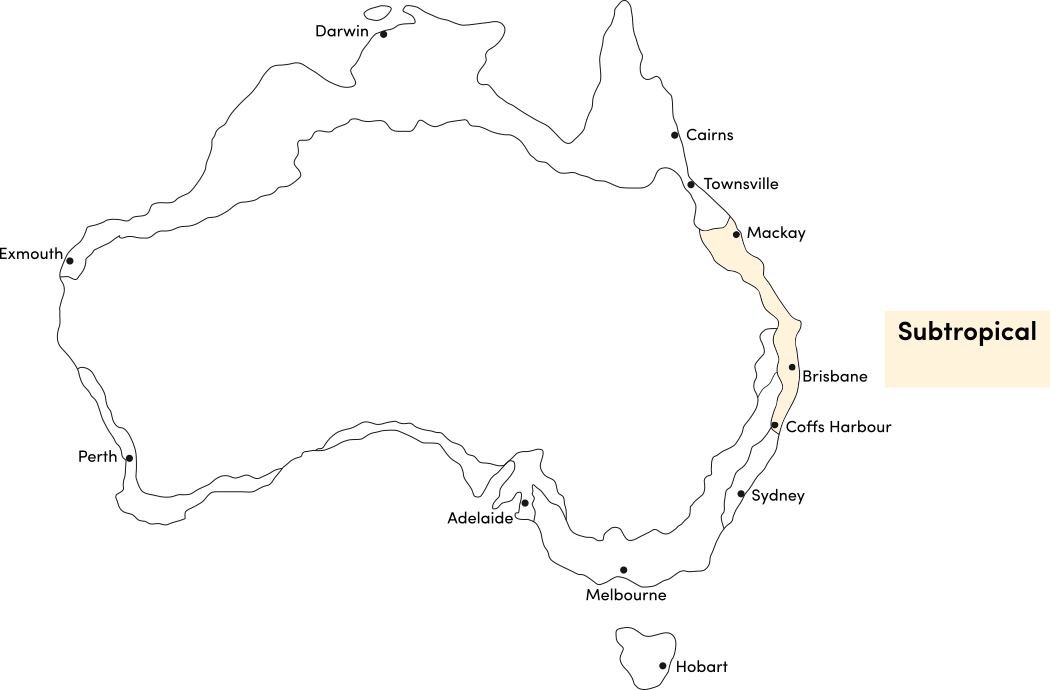
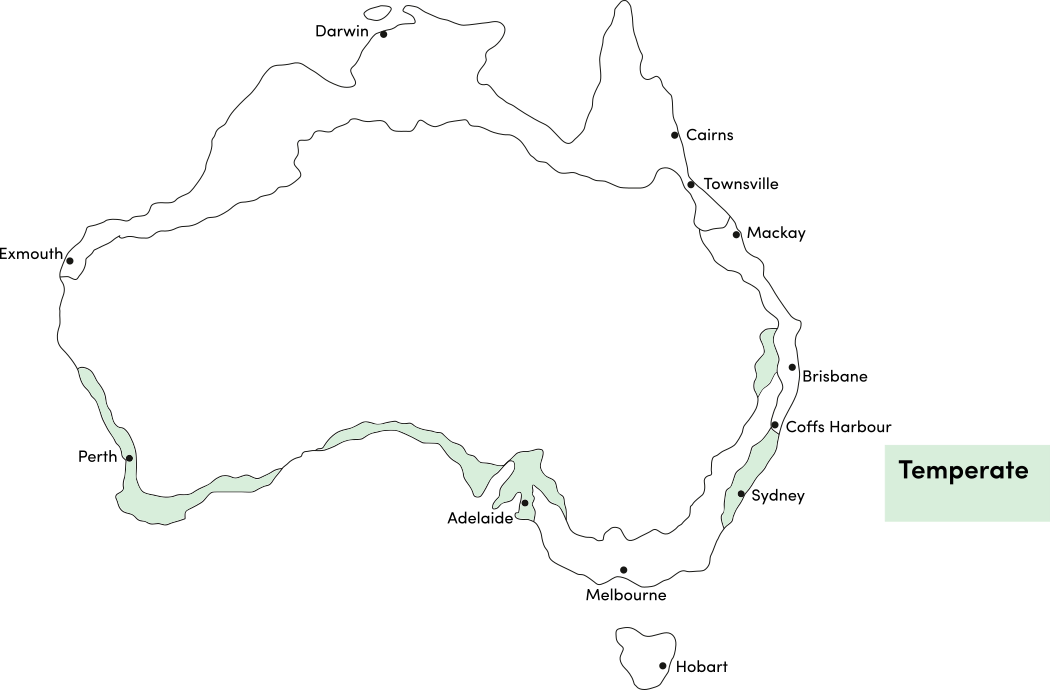
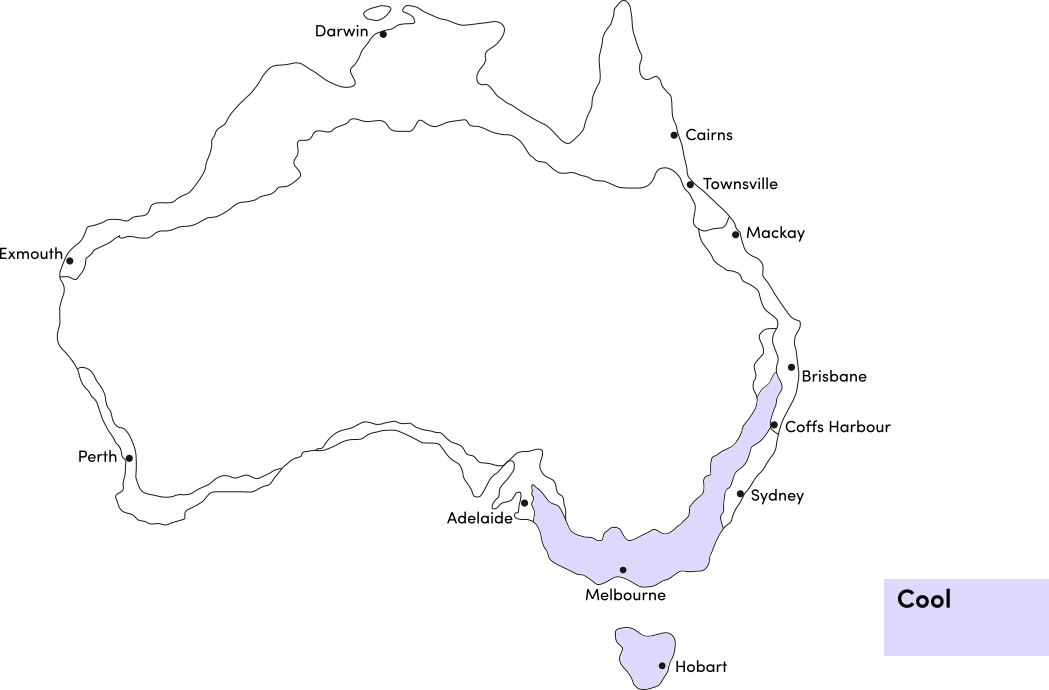
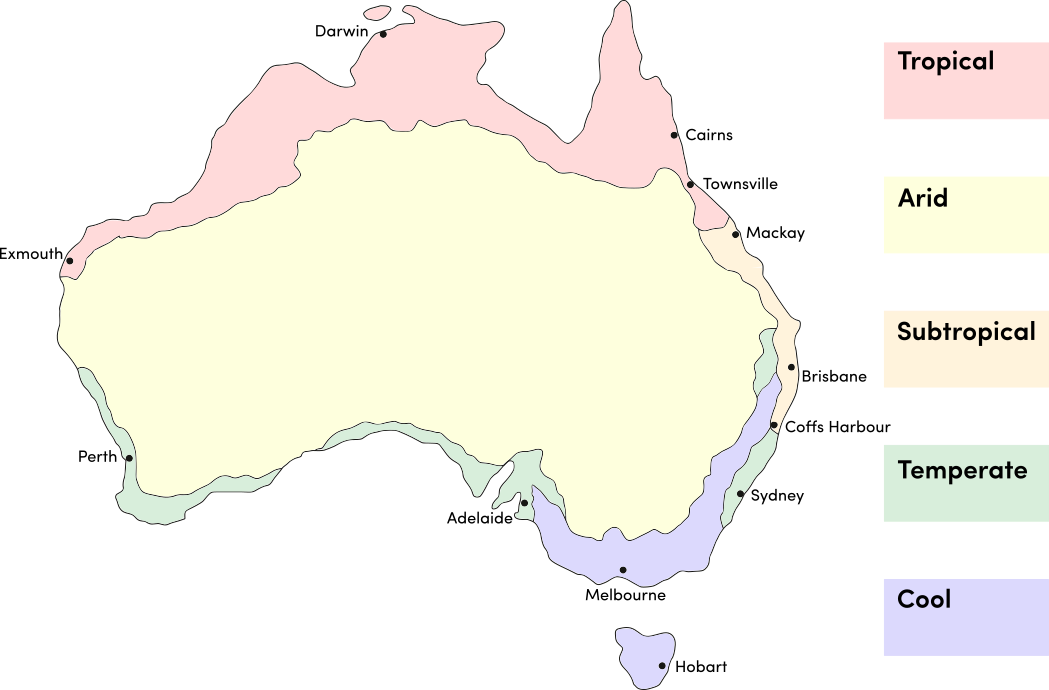
Strawberry spinach is a warm season crop. Use the table below to identify the best time of year to sow strawberry spinach seeds in your climate.
| JAN | FEB | MAR | APR | MAY | JUN | JUL | AUG | SEP | OCT | NOV | DEC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cool | ||||||||||||
| Temperate | ||||||||||||
| Sub-Tropical | ||||||||||||
| Tropical | ||||||||||||
| Arid |
Preparation
Strawberry spinach plants are best grown in full sun or part shade. Choose a location that will receive at least 3 hours of full sun each day.
Strawberry spinach plants commonly self-seed in the garden. Self-seeding plants drop seeds onto the soil at the end of the season that may germinate and grow without help the following season. Choose a position where new plants will be welcome. If you do not want strawberry spinach to become established in your garden, deadhead plants before they can drop seed or grow them in containers.
Strawberry spinach plants need a well drained soil enriched with plenty of organic matter. Prepare soil by weeding it thoroughly, digging it over to loosen it and adding aged animal manure or compost. Keep the area free of weeds until planting. Learn more about preparing soil for planting here.
Strawberry spinach plants can be grown in containers. If possible choose a variety that’s recommended for container growing. Use a good quality potting mix and make sure your container is large enough for mature plants; a minimum of 20 litres is recommended for strawberry spinach. During the growing season, keep in mind that container grown plants may need additional fertiliser to encourage healthy growth.
How to Sow Strawberry spinach Seeds
Strawberry spinach seeds do not require any treatment (eg soaking, stratification) before sowing.
Strawberry spinach seeds grow best when they are raised in trays or other containers and transplanted to the garden once established.
- Fill trays, punnets or jiffy pots with a good quality seed-raising mix, or use soil starter pellets.
- Sow seeds 3mm deep.
- Keep soil moist but never wet or dry.
- Seeds should germinate in around 7-14 days at a soil temperature of 18-22°C.
- Transplant seedlings to the garden once they have their first true leaves and are large enough to handle (usually 5-10cm tall).
- Plant out, spacing plants 100cm apart.
Strawberry spinach is a half hardy crop. Mature plants will survive light frosts but seedlings need protection until they are established. Do not transplant seedlings or sow seeds outside until all danger of frost has passed.
How to Grow Strawberry spinach
Strawberry spinach plants may need watering during the growing season. Water when the soil is dry about 5cm below the surface (test this by scratching away a little soil with your finger). Water deeply in the early morning or late afternoon. Avoid watering the leaves of plants to avoid fungal diseases. Learn more about watering here.
If soil was well prepared no extra fertiliser should be necessary. In poor soil or to give your plants an extra boost, application of a balanced fertiliser or one formulated for fruit and vegetables can be beneficial:
- Apply slow release fertiliser at the recommended rate when transplanting or when seedlings are 5-10cm tall.
- Apply liquid fertiliser at the recommended rate and frequency while plants are fruiting or flowering.
How to Harvest Strawberry spinach
Strawberry spinach should be ready to harvest in approximately 50 days.
Leaves are ready to harvest when they are large enough to eat, and can be harvested as needed. Harvest leaves by pinching off the outer leaves, leaving some on the plant for future growth. Strawberry spinach leaves can be stored short term in a perforated plastic bag in the fridge.
Berries are ready to harvest when they turn red. Harvest fruit by cutting with snips/secateurs or by twisting to separate from the stem. Harvest regularly to encourage more fruit. Berries are best eaten soon after harvest. For long term storage they can be frozen.
Common Problems when Growing Strawberry spinach
Like all plants, strawberry spinach is susceptible to some pests, diseases and other problems. Below is a list of the most common problems gardeners encounter when growing strawberry spinach plants:
 Downy mildew is a fungal disease that causes yellow to grey-brown patches on leaves, especially the undersides. Water plants at soil level (not on the leaves), remove and destroy affected leaves and do not overcrowd plants to ensure adequate air flow. If problems persist, spray with a homemade milk spray or fungicide.
Downy mildew is a fungal disease that causes yellow to grey-brown patches on leaves, especially the undersides. Water plants at soil level (not on the leaves), remove and destroy affected leaves and do not overcrowd plants to ensure adequate air flow. If problems persist, spray with a homemade milk spray or fungicide.
.png)